Data Handling

Introduction
Data handling is considered one of the most important topics in statistics as it deals with collecting sets of data, maintaining security, and the preservation of the research data. The data here is a set of numbers that help in analyzing that particular set or sets of data. Data handling can be represented visually in the form of graphs.
Definition of Data handling
Data Handling is the process of gathering, recording, and presenting information in a way that is helpful to analyze, make predictions and choices. Anything that can be grouped based on certain comparable parameters can be thought of as data. Parameters mean the context in which the comparison is made between the objects. Data handling is usually represented in the form of pictographs, bar graphs, pie charts, histograms, line graphs, stem and leaf plots, etc. All of them have a different purpose to serve.
- The constituents of air are presented with different colors in the form of parts of a pie.
Types of Data
Data handling is performed depending on the types of data. Data is classified into two types, such as Quantitative Data and Qualitative Data. Quantitative data gives numerical information, while qualitative data gives descriptive information about anything. Quantitative can be either discrete or continuous data.
Qualitative Data.
This data is descriptive and subjective, and is collected through interviews, focus groups, surveys, and observations. It can provide insights into people’s thoughts, feelings, and interactions with their environment, and can help you understand the “how” and “why” of human behavior.
Quantitative Data
This data is numeric and objective, and is collected through surveys, experiments, and statistical models. It can be counted or measured in numerical values, and can help you quantify variables and analyze statistical relationships. Examples of quantitative data include height, weight, age, BMI
Important Terms in Data Handling
In data handling, there are 4 important terms or most frequently used terms that make it simple to understand the concept better. The terms are:
- Data: It is the collection of numerical figures of any kind of information
- Raw Data: The observation gathered initially is called the raw data.
- Range: It is the difference between the highest and lowest values in the data collection.
- Statistics: It deals with the collection, representation, analysis, and interpretation of numerical data.
Steps Involved in Data Handling
Following are the steps to follow in data handling:
| Steps | Details |
| Purpose | The problem or purpose is identified and well defined. |
| Collection of Data | Data relevant to the purpose is collected. |
| Presentation of Data | The collected data is to be presented in a form that is meaningful and easy to understand. It could be in the form of a simple table or tally marks etc. |
| Graphical Representation of Data | Visual representation makes analysis and understanding of trends quicker and has a much greater impact. |
| Analyzing the Data | The data undergoes inspection to derive useful and necessary information that helps in taking further actions. |
| Conclusion/Inference | Here we provide a solution to our problem statement based on the analysis of the data. |
Graphical Representation of Data
Data handling can be represented in a number of graphical ways. Here is a list of various types of graphical representations of data that are very effective in data handling.
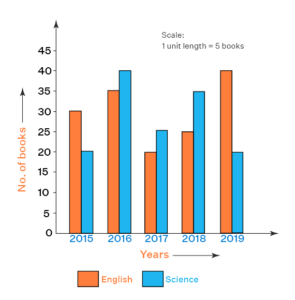
Bar Graphs
Bar Graphs Represent data in the form of vertical or horizontal bars showing data with rectangular bars and the heights of bars are proportional to the values that they represent. Bar graphs help in the comparison of data and this type of graph is most widely used in statistics.
Pictographs or Picture Graphs
Pictograph is a type of graph where information is represented in the form of pictures, icons, or symbols. It is the simplest form of representing data in statistics and data handling. Since the use of images and symbols are more in a pictograph, interpreting data is made easy along with representing a large number of data.
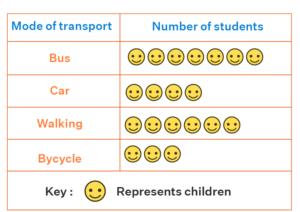
Line Graphs
In data handling the data represented in the form of a line on a graph is the line graph. The graph helps in showcasing the different trends or changes in the data. The line segment plotted on the graph is constructed by connecting individual data points together. 
Pie Charts
A pie chart is data represented in a circular graph divided into smaller sectors to denote certain information. Pie charts help in showcasing the profit and loss for a business, while in school in showcasing the number depending on the data. This kind of chart is widely used in marketing sales.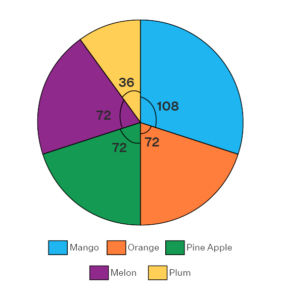
Interactive Simulations
At home, it’s possible to make learning fresh and engaging by encouraging kids to explore topics they are passionate about and allowing them to choose their own data recording techniques. With the help of our interactive simulations, students can create various types of graphs and charts, gaining hands-on experience in understanding which types of graphs are most suitable for representing different categories of data. This approach not only empowers them to take ownership of their learning but also deepens their understanding of data handling by connecting it to their interests and real-world applications.
Real-Life Applications of Data Handling
- Education: Teachers use data handling to assess student performance. By collecting scores, organizing them in a table, and analyzing trends, educators can identify areas where students excel or need improvement.
- Healthcare: Hospitals collect patient data to track health trends, manage resources, and improve care. Data handling helps in predicting disease outbreaks by analyzing patterns in patient data.
- Business: Companies use data to understand customer behavior, manage inventory, and optimize operations. For example, sales data is analyzed to determine which products are most popular and when.
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists collect data on temperature, humidity, and wind speed. By analyzing this data, they can predict weather patterns, helping people prepare for different weather conditions.
- Sports: Coaches and analysts collect and analyze data on player performance, team statistics, and opponent strategies to make informed decisions during games and training.




Responses